Basic steel production processes and principles
Everyone knows that common types of steel such as rebar steel, shaped steel, box steel, steel plates or steel pipes are extremely important materials, commonly used in current construction projects in domestic and oversea area. So which factors the steel production process must comply with? Let CCN explain through this article.
Table of Contents
1. Principles of steel production
2. How many stages does the steel production process include?
2.1. Phase 1: Carry out iron ore processing
2.2. Stage 2: Create a stream of steel when molten
2.3. Stage 3: Casting the next fuel
2.4. Stage 4: Hot rolling and cold rolling
2.5. Stage 5: Galvanized steel pipes and steel coils
Principles of steel production
– Raw materials: steel production is cast iron, scrap iron, oxygen gas.
– Principle: steel production is to oxidize some metals and non-metals to remove most of the elements carbon, silicon, manganese, etc. from cast iron.
– Process: steel smelting is carried out in a Bet-semer furnace. Oxygen gas oxidizes elements in cast iron such as C, Mn, Si, etc.
The product obtained is steel.
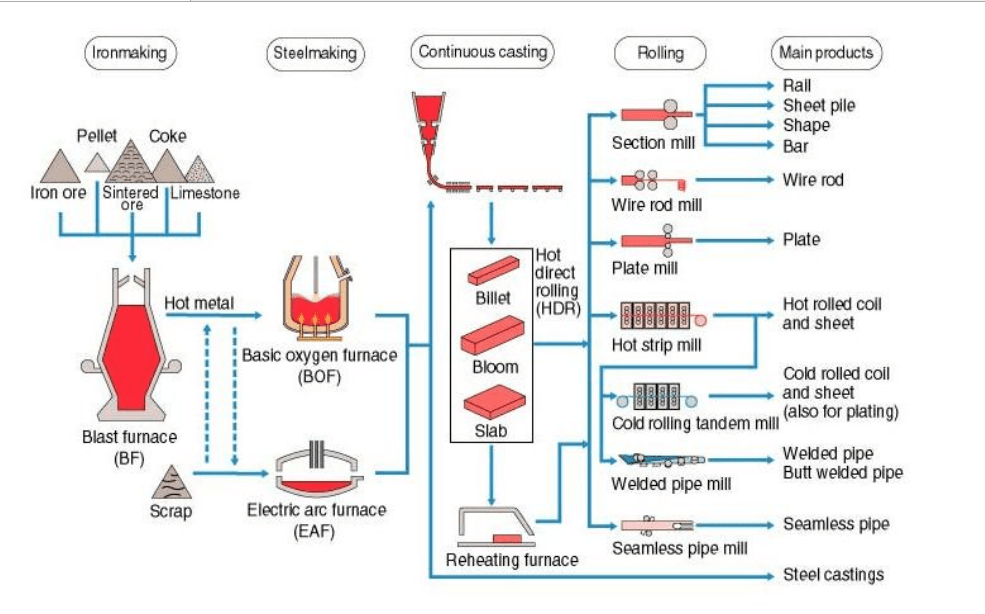
Steel production process
In terms of details, the principles of steel production are not too complicated. This is the process of refining, melting and alloying at a temperature of about 1600 degrees Celsius (corresponding to 2900 degrees F) in molten conditions. All starting chemical reactions will take place in the correct order.
The process of that principle includes many interwoven reactions, requiring the use of process models. From there, there is a proper analysis and analysis of a variety of options to optimize the reactions leading to the most effective steel production process.
How many stages does the steel production process include?
In fact, the steel production process goes through all 5 main stages. Thanks to that process, quality products are produced, meeting the needs of different construction and industrial projects. Learn specifically about the 5 stages as follows:
Phase 1: Carry out iron ore processing
The first step to be done is to bring ores mined underground such as iron ore, pellets, sintered ore and additives such as limestone, coke and steel,... into the top of the mine. furnace. Right here, the mixture of these ingredients will be heated at a certain temperature level, to create a stream of molten metal.
The temperature in the furnace will increase to reach 2000 degrees Celsius, the iron ore will quickly become molten black steel at the bottom of the furnace. Black steel contains carbon, sulfur, silicon as well as many other impurities.

Phase 2: Create a stream of steel when molten
The accepted molten metal obtained at each processing stage will be sent to the base furnace or electric arc furnace. At this time, molten steel is processed and separated from impurities. From there, create a correlation between chemical composition in the steel production process.
For example: If you want to create steel grade SD 390, the chemical composition will be adjusted according to regulations to produce steel grade SD390.

Phase 3: Casting the next fuel
Using molten steel, it is sent to the ingot furnace in stage 2. Immediately after that, 3 basic types of embryos immediately appeared:
– Bar billet: billet with cross section 100×100, 125x 125, length 6-9-12m. Usually used to roll or draw rolled steel as well as rebar.
– Billet: Usually used to roll out hot rolled steel coils, hot rolled steel sheets, cold rolled steel coils or shaped steel.
– Bloom embryos: Applied like 2 types of bar embryos and slab embryos.
After the embryo is cast, it can then be left in two states: hot and cool. In particular, the hot state will maintain the workpiece at a high temperature and then send it straight to hot rolling. On the contrary, if the cold state of the billet is to be sold or transferred to another factory to reheat, then remember to bring it to the cold rolling factory and continue cold rolling production.
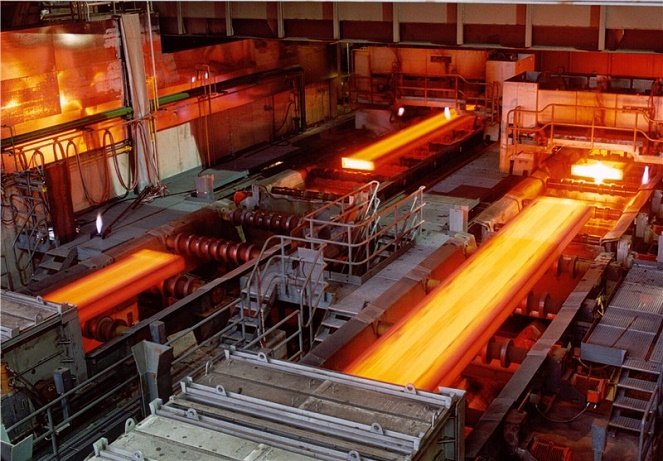

Phase 4: Hot rolling and cold rolling
By compliancing with steel production principles, at this stage, billets are brought into the factory for the purpose of rolling out various construction steel products:
– Bring the billet into the shaped steel factory, from there roll out super products of rail steel or trough sheet steel, I, U, V shaped steel or bar steel.
– Bring the billet right into the steel factory to roll out smooth rolled steel in construction.
– Bring the billets right into the steel plate factory to roll out cast steel plates.
– Bring the billet into the hot rolling steel factory and the billet will be rolled into hot rolled steel coils.
In case the rolled steel is cold rolled, then remember to lower the temperature to the most suitable level. After that, continue to pass through the rust removal line before preparing to put it into the next 5-rack rolling machine.
Each rolling rack seems to be equipped with its own X-ray thickness measuring machine and AGC automatic thickness calibration device.
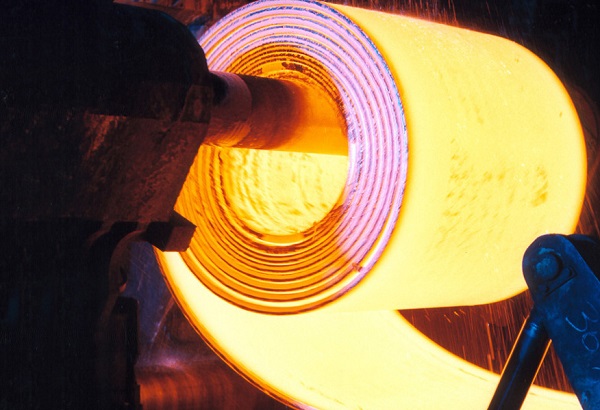

Phase 5: Galvanized steel pipes and steel coils
Cold rolled steel is obtained in stage 4, thanks to NOF technology and successfully undergoes the galvanizing process. Accordingly, complete the roll surface one last time as well as add a layer of plating with high adhesion on the surface.
The zinc coating protects steel against acid corrosion, while also increasing the longevity of the product.
People will use high-frequency welding technology when bending pipes, to ensure smoothness and shine for each weld line and edge of the steel. All cold rolled steel products such as rectangular steel boxes, round steel boxes and square boxes are produced in many different designs and sizes.

Steel boxes come in many different designs and sizes
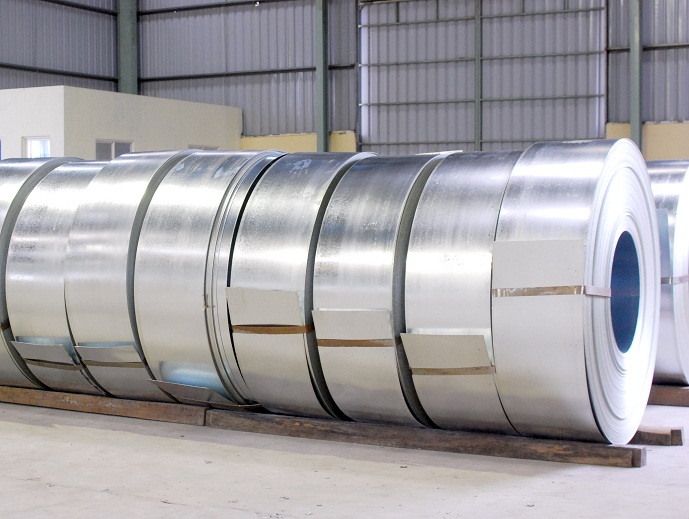

Galvanized steel coil
Above is all information about the steel production process and principles applied by almost all steel factories of all famous steel brands in Vietnam. If you wish to open a mini steel factory, you can check the above information to start your work.
.png)
-480x320.jpg)


Write a comment